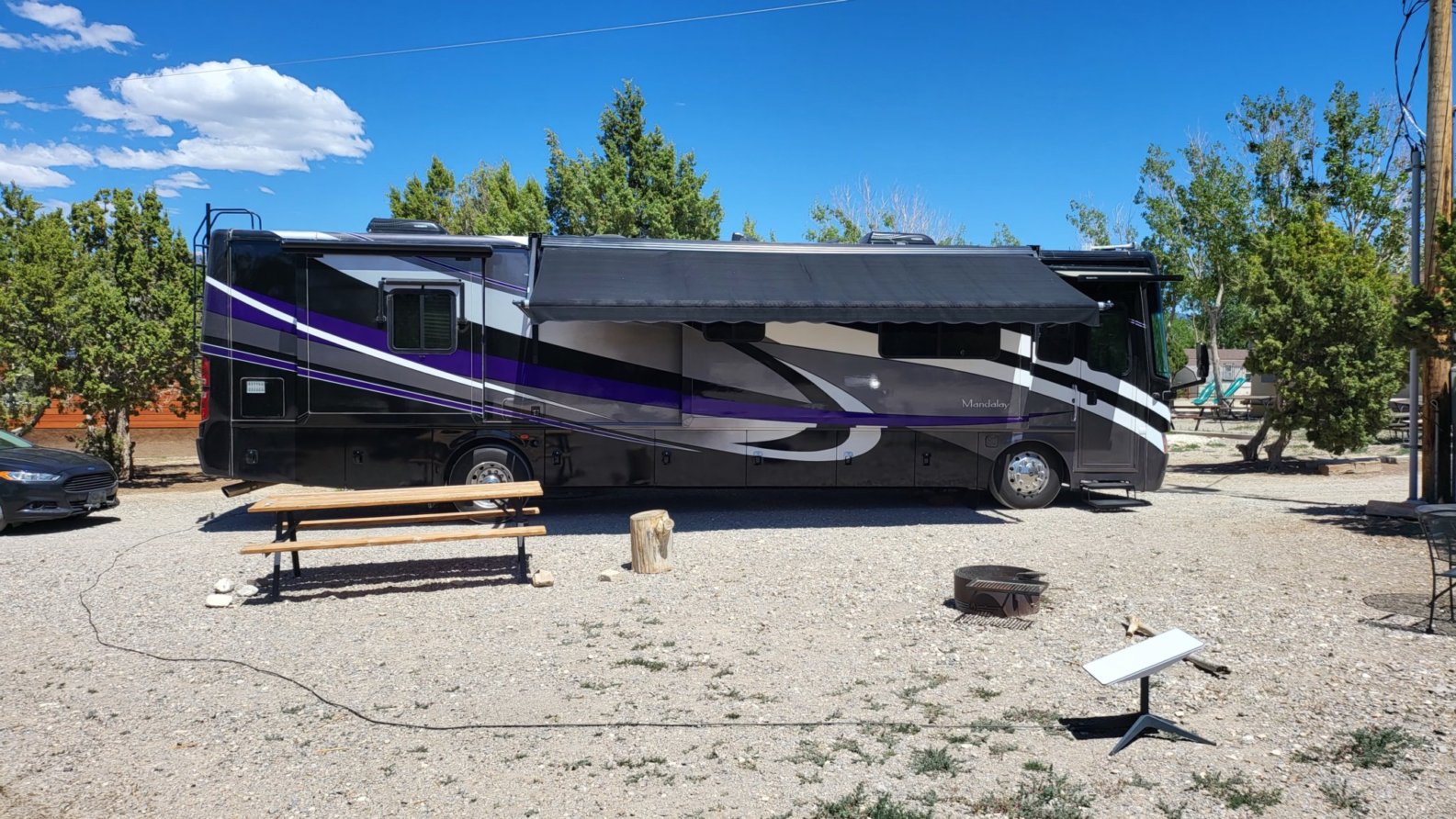
California's $2.717 trillion economy is larger than that of any other state. Overall, California pays more in taxes than any other state — $405 billion, or about 12% of all taxes paid in the country. If it were a country, California would be the 5th largest economy in the world, and the 36th most populous. The Greater Los Angeles Area and the San Francisco Bay Area are the nation's second- and third-largest urban economies, after the New York metropolitan area. The San Francisco Bay Areacombined statistical area has the nation's highest GDP per capita and is home to four of the world's ten largest companies by market capitalization and four of the world's ten richest people.
California is considered a global trendsetter in popular culture, innovation, and politics. It is the origin of the film industry, the hippie counterculture, the Internet, and the personal computer, among others. The San Francisco Bay Area and the Greater Los Angeles Area are widely seen as centers of the global technology and entertainment industries, respectively. California has a very diverse economy: 58% of the state's economy is centered on finance, government, real estate services, technology, and professional, scientific and technical business services. Although it accounts for only 1.5% of the state's economy, California's agriculture industry has the highest output of any U.S. state.
California is bordered by Oregon to the north, Nevada, and Arizona to the east, and the Mexican state of Baja California to the south. The state's diverse geography ranges from the Pacific Coast in the west to the Sierra Nevada mountain range in the east, and from the redwood–Douglas fir forests in the northwest to the Mojave Desert in the southeast. The Central Valley, a major agricultural area, dominates the state's center. Though California is well-known for its warm Mediterranean climate, the large size of the state results in climates that vary from moist temperate rainforest in the north to arid desert in the interior, as well as snowy alpine in the mountains.
What is now California was first settled by various Native Californian tribes before being explored by a number of European expeditions during the 16th and 17th centuries. The Spanish Empire then claimed it as part of Alta California in their New Spain colony. The area became a part of Mexico in 1821 following its successful war for independence but was ceded to the United States in 1848 after the Mexican–American War. The western portion of Alta California then was organized and admitted as the 31st state on September 9, 1850. The California Gold Rush starting in 1848 led to dramatic social and demographic changes, with large-scale emigration from the east and abroad with an accompanying economic boom.